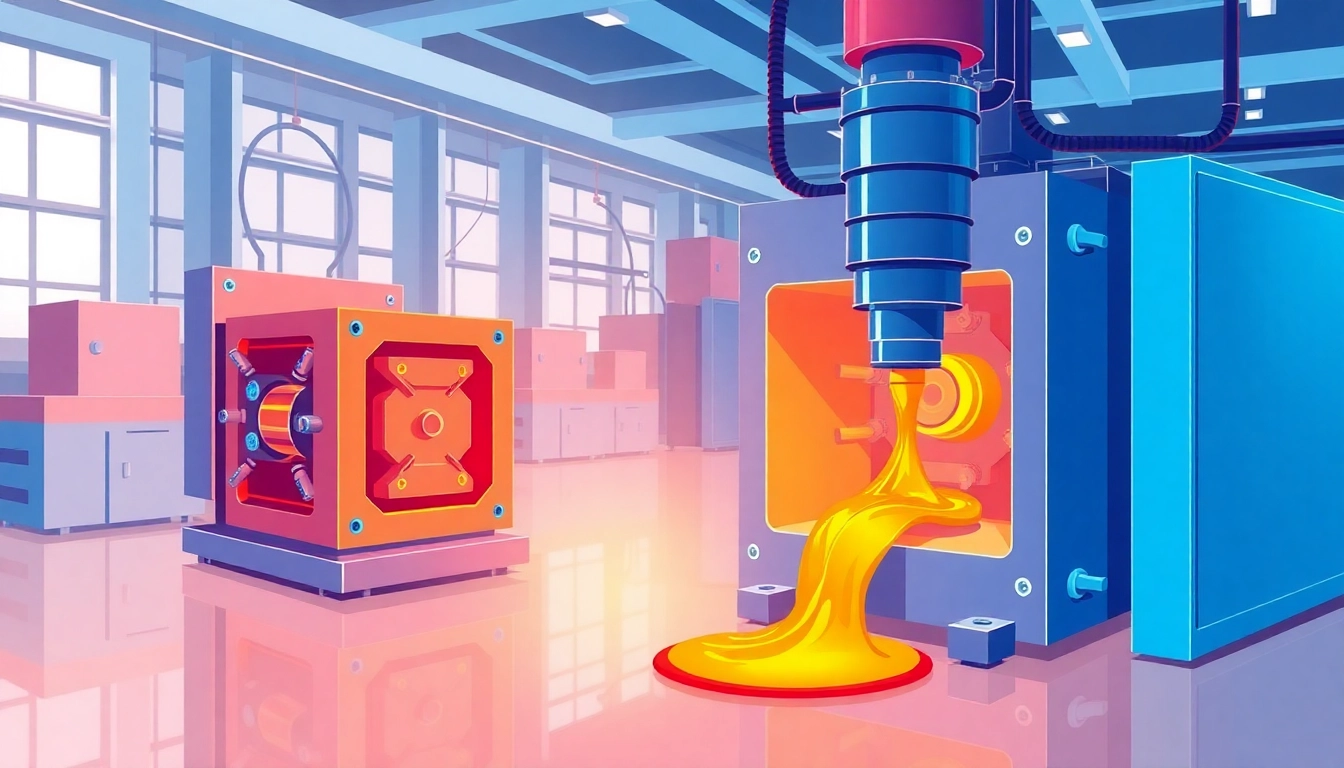
Understanding the Manufacture of Plastic Parts
The manufacture of plastic parts is a crucial aspect of modern industry, reflecting a blend of engineering, design, and advanced manufacturing processes. As a foundational element in diverse sectors, from automotive to consumer goods, understanding how these parts are made can significantly impact choice and quality in product development. Plastic parts manufacture involves multiple processes and materials tailored to meet specific application needs. With the steady advancement of technology, these methods are rapidly evolving, harnessing new materials and innovative techniques to enhance efficiency and sustainability. For an in-depth look at various manufacturing methods, visit manufacture of plastic parts.
Definition and Importance
Plastic part manufacturing refers to the processes used to create components made from a variety of plastic resins. These methods are vital for producing everything from tiny, intricate components used in electronics to large, structural parts utilized in automotive and aerospace applications. The importance of plastic part production can be understood through several key factors:
- Versatility: Plastics can be molded into almost any shape, allowing for creative flexibility in design.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Mass production methods can lower manufacturing costs, making plastic parts affordable for a range of applications.
- Lightweight Advantage: Compared to metals, plastics are lighter, which can enhance energy efficiency in transportation and other applications.
- Durability: Many plastics are resistant to corrosion, moisture, and chemicals, extending the lifespan of products.
Key Materials Used
The manufacture of plastic parts involves several types of materials that are selected based on the desired properties of the final product. The most commonly used materials in plastic manufacturing include:
- Polyethylene (PE): Known for its flexibility and chemical resistance, PE is widely used in packaging and containers.
- Polystyrene (PS): Often used for disposable cutlery and packaging, PS is lightweight and easy to mold.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): A strong and durable plastic commonly used in construction and piping.
- Polypropylene (PP): Valued for its toughness and resistance to heat, PP is used in products ranging from automotive parts to medical devices.
- Thermoplastic Elastomers (TPE): A unique blend of rubber-like and plastic properties, TPE is used in a variety of consumer products.
Typical Applications of Plastic Parts
The applications of plastic parts are broad and varied, encompassing many industries and functionalities. Common examples include:
- Automotive: Dashboard components, bumpers, and fuel tanks are often made from molded plastics for weight reduction and cost efficiency.
- Consumer Electronics: Casings, connectors, and internal components frequently use plastics to ensure lightweight, durable products.
- Medical Devices: From syringes to surgical trays, plastics are essential for their biocompatibility and ease of sterilization.
- Household Goods: Kitchenware, storage containers, and toys commonly rely on plastics for their durability and affordability.
Main Manufacturing Processes
Understanding the different manufacturing processes for plastic parts is crucial for selecting the right technique based on product requirements and specifications. Below, we explore the primary methods used in the industry.
Injection Molding Explained
Injection molding is one of the most prevalent methods for producing plastic parts. In this process, plastic is heated until it melts and then injected into a mold under pressure.
- Material Preparation: The process begins with pellets of thermoplastic resin being fed into a heated barrel where they are melted.
- Injection: The molten plastic is injected rapidly into a mold, which determines the shape of the final product.
- Cooling: After injection, the plastic is cooled within the mold, solidifying into its final form.
- Mold Release: Once cooled, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
Injection molding is highly efficient for mass production, offering high precision and repeatability, making it ideal for complex parts and high volumes. However, tooling design can be expensive and time-consuming.
The Role of Extrusion in Plastic Formation
Extrusion is another critical method in plastic manufacturing, commonly used for creating continuous lengths of plastic products, such as pipes, sheets, and films.
- Material Feeding: Raw plastic pellets are fed into an extruder, where they are heated to a molten state.
- Forming: The molten plastic is forced through a die that shapes it into the desired profile.
- Cooling: The extruded plastic is cooled, typically with air or water, to retain its shape.
- Cutting or Winding: Finally, the continuous length is either cut into specific lengths or wound onto reels.
Extrusion is advantageous because it allows for the large-scale production of uniform products with minimal waste. It is widely used in construction and packaging industries.
Rotational Molding Techniques
Rotational molding, or roto-molding, is a manufacturing process specifically used for hollow plastic parts. It involves a unique method that can produce complex shapes with uniform wall thickness.
- Material Placement: A measured amount of powdered resin is placed in a mold.
- Heating and Rotating: The mold is heated while being rotated on multiple axes, allowing the powder to evenly coat the inside surfaces of the mold as it melts.
- Cooling: Once the material is uniformly distributed and adhered to the mold, it is allowed to cool.
- Demolding: The mold is opened, and the hollow plastic part is removed.
This process is particularly useful for producing large items, such as tanks and playground equipment, where wall thickness uniformity is critical.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate manufacturing process for plastic parts is essential for achieving desired outcomes in terms of design, performance, and cost. Several factors must be considered during this decision-making process.
Factors Influencing Process Selection
Several critical factors influence the choice of manufacturing processes for plastic parts, including:
- Material Properties: The characteristics of the plastic material, such as melting temperature and flow characteristics, will dictate the feasible manufacturing methods.
- Complexity of Design: The complexity of the part design may necessitate advanced techniques such as injection molding or rotational molding.
- Production Volume: High production volumes typically favor methods like injection molding, whereas lower volumes may lead to considerations of CNC machining or 3D printing.
Cost Considerations
Cost is another significant variable in the manufacturing process selection. Each method has unique cost implications that should be analyzed:
- Tooling Costs: Injection molding requires expensive molds, which can be justified for high-volume runs but may be prohibitive for low volumes.
- Material Costs: Different materials incur varying costs, and the choice of material can drastically affect overall production expenses.
- Labor Expenses: The complexity of the manufacturing process can dictate labor costs, with highly automated processes generally incurring lower labor costs.
Volume Requirements and Production Speed
Understanding the volume requirements for plastic parts is essential for selecting the right manufacturing process. Each method offers different speed efficiencies that should be matched to production needs:
- High Volume Needs: Injection molding excels at producing large quantities of identical parts quickly.
- Prototype Development: For creating prototypes or small batches, processes like 3D printing or CNC machining may be more effective and cost-efficient.
Quality Control in Plastic Manufacturing
Quality control is a critical aspect of plastic manufacturing, ensuring that the final products meet the required standards and specifications. The integration of effective quality control methods is essential for maintaining product integrity and consumer safety.
Testing and Quality Assurance Methods
There are several methods to ensure the quality of plastic parts during manufacturing:
- Visual Inspections: Regular inspections can catch surface defects, color discrepancies, and misalignments early in the manufacturing process.
- Dimensional Testing: Using tools such as calipers and gauges helps manufacturers verify the part dimensions against specifications.
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluating properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, and thermal stability ensures that the parts perform as intended.
Common Defects and Solutions
Understanding common defects that occur in plastic parts manufacturing can help mitigate issues:
- Bubbles or Voids: These can arise from gas entrapment during molding. Adjusting the injection speed and pressure can alleviate this issue.
- Warping: This defect often occurs during the cooling phase. Maintaining consistent temperature throughout the process can help reduce warping risks.
- Surface Imperfections: Contaminants or bed surfaces can cause superficial issues. Regular cleanings and careful handling of molds can solve this problem.
Ensuring Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is critical in plastic manufacturing, especially for industries like medical devices and food packaging. Manufacturers must adhere to standards set forth by organizations such as:
- ISO (International Organization for Standardization): Provides standards that ensure quality management systems.
- ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials): Establishes standards for material composition and testing methods.
- FDA (Food and Drug Administration): Sets guidelines for materials used in packaging food and medical products.
Future Trends in Plastic Manufacturing
The landscape of plastic manufacturing is continually evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer preferences. Staying informed about emerging trends is essential for manufacturers aiming to remain competitive.
Sustainable Practices in Manufacturing
With increasing environmental concerns, many manufacturers are exploring sustainable practices in plastic production:
- Recyclable Materials: Using materials that are easier to recycle can significantly reduce waste.
- Biodegradable Plastics: Research into biodegradable plastics is expanding, offering alternatives that mitigate pollution.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient processes helps reduce the carbon footprint associated with production.
Technological Innovations
Technological advancements are transforming plastic manufacturing processes:
- Additive Manufacturing: 3D printing technology is gaining traction for prototyping and manufacturing small batches.
- Smart Manufacturing Technologies: The integration of IoT sensors and AI enhances monitoring and efficiency in production lines.
Market Projections for Plastic Parts
The market for plastic parts continues to expand, driven by demand across various industries:
- Automotive Growth: Increasing focus on lightweight vehicles is fueling the demand for plastic parts.
- Consumer Electronics Demand: The ongoing rise in technology products ensures that plastic parts remain in high demand.
As the industry progresses, manufacturers must adapt to evolving consumer preferences, market dynamics, and technological innovations to remain competitive and meet sustainability goals.